gridpath
Welcome to GridPath

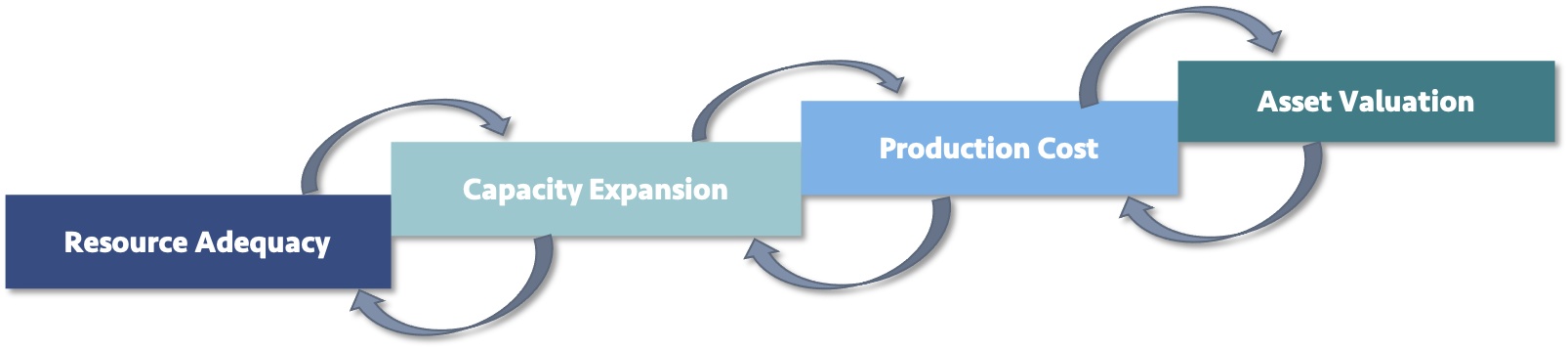
GridPath is a versatile power-system planning platform capable of a range of planning approaches including production-cost, capacity-expansion, asset-valuation, and reliability modeling.
Documentation
GridPath’s documentation is hosted on Read the Docs.
Installation
Python
GridPath is tested on Python 3.9, 3.10, and 3.11. Get one of those Python versions here.
GridPath Python environment
You should create a Python environment for your GridPath installation, e.g. via
venv, a lightweight environment manager
that is part of the standard Python distribution. Make sure to create activate the environment before installing GridPath.
Install GridPath from PyPi
Once you have created and activated the GridPath Python environment, you can install the latest version of GridPath from PyPi with:
pip install GridPath
Install GridPath from source
You can alternatively download the GridPath source code and install from source.
pip install .[all]
NOTE: If you plan to edit the GridPath code, you should install with the -e flag.
Solver
You will need a solver to use this platform. GridPath assumes you will be using Cbc (Coin-or branch and cut) by default, but you can specify a different solver.
Usage
The gridpath_run and gridpath_run_e2e commands
If you install GridPath via the setup script following the instructions above,
you can use the command gridpath_run to run a scenario from any directory
– as long as your GridPath Python environment is enabled – as follows:
gridpath_run --scenario SCENARIO_NAME --scenario_location
/PATH/TO/SCENARIO
If you are using the database, you can use the command gridpath_run_e2e to
run GridPath end-to-end, i.e. get inputs for the scenario from the database,
solve the scenario problem, import the results into the database, and
process them. Refer to the documentation for how to build the database.
gridpath_run_e2e --scenario SCENARIO_NAME --scenario_location
/PATH/TO/SCENARIO
To see usage and other optional arguments, e.g. how to specify a solver, check the help menu, e.g.:
gridpath_run --help
